leetcode-ds
[TOC]
1. 数组(含二维)和字符串
题型一: 同向双指针
[283] 移动零 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/move-zeroes/ 🌟🌟
// 经典双指针
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
int i = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < nums.size(); j++){
if(nums[j] != 0){ // 当不为零的时候,
nums[i] = nums[j]; // 直接进行替换
i++;
}
}
while(i < nums.size()) nums[i++] = 0;
}[27] 移除元素 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-element/
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int i = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < nums.size(); j++){
if(nums[j] != val){
nums[i] = nums[j];
i++;
}
}
return i;
}26]. 删除排序数组中的重复项
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0) return 0;
int i = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < nums.size(); j++){
if(nums[i] != nums[j]){
i++;
nums[i] = nums[j];
}
}
return i+1;
}[80] 删除排序数组中的重复项 II https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array-ii/
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() <= 2) return nums.size();
int p = 1;
int cnt = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++){
if(nums[i] == nums[i-1]) cnt++;
else cnt = 1;
if(cnt <= 2) nums[p++] = nums[i];
}
return p;
}[58] 最后一个单词的长度 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/length-of-last-word/
int lengthOfLastWord(string s) {
int res = 0;
int pos = s.size() - 1;
while(pos >= 0 && s[pos] == ' ') pos--;
while(pos >= 0 && s[pos--] != ' ') res++;
return res;
}[lcof 21] 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/diao-zheng-shu-zu-shun-xu-shi-qi-shu-wei-yu-ou-shu-qian-mian-lcof/)
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
while(i < j){
while(i <j && nums[i] % 2 == 1) i++;
while(i < j && nums[j] % 2 == 0) j--;
swap(nums[i++], nums[j--]);
}
return nums;
}题型二: 相向双指针
[167] 两数之和 II - 输入有序数组 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum-ii-input-array-is-sorted/ 🌟🌟
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& numbers, int target) {
int begin = 0, end = numbers.size() - 1;
while(begin < end){
int s = numbers[begin] + numbers[end];
if(s == target) return {begin+1, end+1};
else if(s > target) end--;
else begin++;
}
return {-1, -1};
}[15] 三数之和 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/ 🌟🌟
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
set<vector<int> > res; // set 去重
if(nums.size()==0) return {};
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++){
if(nums[i] > 0) continue; // 剪枝
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue;
int l = i + 1, r = nums.size()-1;
while(l < r){
if(nums[l] + nums[r] == -1 * nums[i]){
res.insert({nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]});
l++;
r--;
}else if(nums[l] + nums[r] > -1 * nums[i]){
r--;
}else{
l++;
}
}
}
return vector<vector<int>>(res.begin(), res.end());
}[18] 四数之和 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum/
vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
set<vector<int> > res;
if(nums.size() < 3) return {};
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n - 3; i++){
for(int j = i + 1; j < n-2; j++){
int t = target - (nums[i] + nums[j]);
int l = j + 1, r = n-1;
while(l < r){
if(nums[l] + nums[r] == t){
res.insert({nums[i], nums[j], nums[l], nums[r]});
l++;
r--;
}else if(nums[l] + nums[r] > t){
r--;
}else{
l++;
}
}
}
}
return vector<vector<int> >(res.begin(), res.end());
}[16] 最接近的三数之和 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum-closest/
int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int res = 0;
int min_diff = INT_MAX;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n-2; i++){
int l = i+1, r = n-1;
while(l < r){
int s = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r];
if(abs(s - target) < min_diff){
min_diff = abs(s - target);
res = s;
}
if(s == target){
l++;r--;
}else if(s > target){
r--;
}else{
l++;
}
}
}
return res;
}[11] 盛最多水的容器 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/container-with-most-water/
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int l = 0, r = height.size()-1;
int max_water = 0;
while(l < r){
int water = (r-l) * min(height[l], height[r]);
max_water = max(max_water, water);
if(height[l] < height[r]) l++; // 移动短板即可 !!
else r--;
}
return max_water;
}题型三: 二维矩阵
[59]. 螺旋矩阵 II https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/
vector<vector<int>> generateMatrix(int n) {
vector<vector<int> > matrix(n, vector<int>(n));
int row_b = 0, row_e = n - 1;
int col_b = 0, col_e= n - 1;
int val = 1;
while(row_b<= row_e && col_b <= col_e){
for(int i = col_b; i <= col_e; i++) matrix[row_b][i] = val++;
row_b++;
for(int i = row_b; i <= row_e; i++) matrix[i][col_e] = val++;
col_e--;
for(int i = col_e; i >= col_b; i--) matrix[row_e][i] = val++;
row_e--;
for(int i = row_e; i >= row_b; i--) matrix[i][col_b] = val++;
col_b++;
}
return matrix;
}[54] 螺旋矩阵 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix/
// 行列不同,可以在每一行/列 都进行一次弹出判断
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
vector<int> res;
if(matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0) return res;
int start_r = 0, end_r = matrix.size() - 1;
int start_c = 0, end_c = matrix[0].size() - 1;
while(true){ // 这里退出的条件放在每个内层循环里面
for(int i = start_c; i <= end_c; i++) res.push_back(matrix[start_r][i]);
if(++start_r > end_r) break;
for(int i = start_r; i <= end_r; i++) res.push_back(matrix[i][end_c]);
if(--end_c < start_c) break;
for(int i = end_c; i >= start_c; i--) res.push_back(matrix[end_r][i]);
if(--end_r < start_r) break;
for(int i = end_r; i >= start_r; i--) res.push_back(matrix[i][start_c]);
if(++start_c > end_c) break;
}
return res;
}[74] 搜索二维矩阵 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix/
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
if(matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0) return false;
int raw = matrix.size(), col = matrix[0].size();
int i = 0, j = col - 1;
while(i < raw && j >= 0){
if(matrix[i][j] == target) return true;
else if(matrix[i][j] > target) j--;
else i++;
}
return false;
}[48] 旋转图像 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-image/ 🌟🌟
void rotate(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
if(matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0) return;
int row = matrix.size(), col = matrix[0].size();
// 沿主对角线对折
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for(int j = i; j < col; j++){
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);
}
}
// 水平翻转
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < col / 2; j++){
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[i][col-1-j]);
}
}
return;
}[73]. 矩阵置零 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/set-matrix-zeroes/
void setZeroes(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(); // 行
int n = matrix[0].size(); // 列
vector<int> raw(m, 0);
vector<int> col(n, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(matrix[i][j] == 0) raw[i]=1;
if(matrix[i][j] == 0) col[j]=1;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < raw.size(); i++){
if(raw[i])
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
for(int j = 0; j < col.size(); j++){
if(col[j])
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}题型四: 回文与翻转
[9] 回文数 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-number/
bool isPalindrome(int x) {
string str = to_string(x);
int begin = 0, end = str.size()-1;
while(begin < end){
if(str[begin++] != str[end--]) return false;
}
return true;
}[lcof 58] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zuo-xuan-zhuan-zi-fu-chuan-lcof/ 🌟🌟
void reverse(string& s, int i, int j){
while(i < j){
swap(s[i++], s[j--]);
}
}
string reverseLeftWords(string s, int n) {
reverse(s, 0, n-1);
reverse(s, n, s.size() - 1);
reverse(s, 0, s.size() - 1);
return s;
}[557] 反转字符串中的单词 III https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string-iii/
void reverse(string& a, int start, int end){
while(start < end){
swap(a[start++], a[end--]);
}
}
string reverseWords(string s) {
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
while(i < s.size() && s[i] == ' ') i++; // 指向非空
int j = i+1;
while(j < s.size() && s[j] != ' ') j++;
reverse(s, i, j-1);
i = j;
}
return s;
}[lcof 58] 翻转单词顺序 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/fan-zhuan-dan-ci-shun-xu-lcof/
// 全手写: 有点繁琐
string reverseWords(string s) {
// 预处理: 去除首尾字符
s.erase(0, s.find_first_not_of(" "));
s.erase(s.find_last_not_of(" ") + 1);
if(s.empty()) return s; // 可以防止多空格的情况
// 单词拆分
vector<string> vec_word;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size();){
int j = i + 1;
while(j < s.size() && s[j] != ' ') j++;
vec_word.push_back(s.substr(i, j-i));
while(j < s.size() && s[j] == ' ') j++;
i = j;
}
// 连接
string res;
for(int i = vec_word.size()-1; i > 0; i--){
res += vec_word[i];
res += " ";
}
res += vec_word[0];
return res;
}题型五: 字符串和数字交互
[8] 字符串转换整数 (atoi) https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/string-to-integer-atoi/
int myAtoi(string s) {
int pos = 0;
while(s[pos] == ' ') pos++;
int positive = true;
if(s[pos] == '+'){
positive = true;
pos++;
}
else if(s[pos] == '-'){
positive = false;
pos++;
}
long res = 0;
while(isdigit(s[pos])){
res = res * 10 + (s[pos] - '0');
if(res > INT_MAX || res < INT_MIN) break;
pos++;
}
res = positive ? res : -1 * res;
if(res > INT_MAX) return INT_MAX;
if(res < INT_MIN) return INT_MIN;
return (int)res;
}数组中重复的数字
int findRepeatNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
set<int> m_set;
for(auto n:nums){
if(m_set.find(n) == m_set.end())
m_set.insert(n);
else
return n;
}
return 0;
}[lcof 66] 构建乘积数组 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/gou-jian-cheng-ji-shu-zu-lcof/
vector<int> constructArr(vector<int>& a) {
if(a.size() == 0) return {};
int len = a.size();
vector<int> res(a.size(), a[len-1]);
for(int i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--)
res[i] = res[i+1] * a[i];
int m = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < a.size()-1; i++){
res[i] = m * res[i+1];
m *= a[i];
}
res[a.size()-1] = m;
return res;
}[415] 字符串相加 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-strings/ 🌟🌟
string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {
reverse(num1.begin(), num1.end());
reverse(num2.begin(), num2.end());
string res = "";
int c_in = 0;
int i = 0;
while(i < num1.size() || i < num2.size()){
int n1 = i < num1.size() ? num1[i] - '0':0;
int n2 = i < num2.size() ? num2[i] - '0':0;
int s = n1 + n2 + c_in;
c_in = s / 10;
res = res + to_string(s % 10);
i++;
}
if(c_in) res += to_string(c_in);
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}[14] 最长公共前缀 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-common-prefix/
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {
if(strs.size() == 0) return "";
if(strs.size() == 1) return strs[0];
for(int i = 0; i < strs[0].size(); i++){
char c = strs[0][i];
for(int j = 1; j < strs.size(); j++){
if(strs[j].size() < i) return strs[0].substr(0, i);
if(strs[j][i] != c) return strs[0].substr(0, i);
}
}
return strs[0];
}[88] 合并两个有序数组 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/ 🌟🌟
void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) {
nums1.resize(m+n);
int i = m-1, j = n-1, k = m+n-1;
while(i >= 0 && j >= 0){
if(nums1[i] < nums2[j]) nums1[k--] = nums2[j--];
else nums1[k--] = nums1[i--];
}
while(j >= 0) nums1[k--] = nums2[j--];
}[217] 存在重复元素 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contains-duplicate/
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
set<int> m_set(nums.begin(), nums.end());
return nums.size() > m_set.size();
}滑动窗口
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
map<char, int> m_map;
int i = 0;
int max_len = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < s.size(); j++){
if(m_map.find(s[j]) == m_map.end() || m_map[s[j]] < i ){
max_len = max(max_len, j-i+1);
}else{
i = m_map[s[j]] + 1;
}
m_map[s[j]] = j;
}
return max_len;
}[31] 下一个排列 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/next-permutation/
void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {
// 1. 先找出最大的索引 k 满足 nums[k] < nums[k+1],如果不存在,就翻转整个数组
int index1 = -1;
for(int i = nums.size()-2; i >= 0; i--){
if(nums[i] < nums[i+1]){
index1 = i;
break;
}
}
if(index1 == -1){
reverse(nums, 0, nums.size()-1);
return;
}
// 2. 再找出另一个最大索引 l 满足 nums[l] > nums[k];
int index2 = -1;
for(int i = nums.size()-1; i >= 0; i--){
if(nums[i] > nums[index1]){
index2 = i;
break;
}
}
// 3. 交换 nums[l] 和 nums[k];
swap(nums[index1], nums[index2]);
// 4. 最后翻转 nums[k+1:]。
reverse(nums, index1+1, nums.size()-1);
}
void reverse(vector<int> & nums, int start, int end){
while(start < end){
swap(nums[start++], nums[end--]);
}
}[3] 无重复字符的最长子串 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/) 🌟🌟🌟
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int res = 0;
// 用 lookup 来替代滑动窗口, 实现高效去重查询
unordered_set<int> lookup;
int left = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
while(lookup.find(s[i]) != lookup.end()){
lookup.erase(s[left]);
left++;
}
res = max(res, i - left + 1);
lookup.insert(s[i]);
}
return res;
}2. 栈、堆、队列
常见题目类型:
- 设计题就是用栈实现队列、用队列实现栈、设计最小栈
- 基于这几种数据结构来实现某些功能, 比如数据流的中位数、滑动窗口的最大值、第k个最大值
- 单调栈(队列)的应用: 比如接雨水、直方图中的最大矩形
(1) 常见技巧总结
- 不要对空容器(栈、堆、队列进行操作)
- 单调栈/队列的应用是一个挺重要的点。
- 有时入栈的元素时下标 index, 而不是 value,这样更方便操作。因为数组可以直接按照下标进行索引。
栈 : 先进后出
stack<int> m_stack; m_stack.size() m_stack.empty() m_stack.push() m_stack.pop() m_stack.top()队列:先进先出
queue<int> m_queue; m_queue.size() m_queue.empty() m_queue.push() m_queue.pop() m_queue.front()双端队列
deque<int> m_deque; m_deque.size() m_deque.empty() m_deque.front() m_deque.back()
m_deque.push_back() m_deque.pop_back() m_deque.push_front() m_deque.pop_front()优先队列
实现:二叉堆, 最大(小)值 先出的完全二叉树
priority_queue<int> max_heap; // 默认构造最大堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int> > max_heap; // 构造最大堆:less -> max_heap
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > min_heap; // 构造最小堆:greater -> min_heap
max_heap.size() max_heap.empty() max_heap.push() max_heap.pop()
max_heap.top() // 虽然它是一个队列,但是这里去元素不是 front 方法, 而是 top 方法: 返回堆顶(2) 典型例题
类型一: 常规题目
[155] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/min-stack/ 🌟🌟
// 解题思路:
// 使用辅助栈记录栈的最小值
// 当添加元素时, 将待添加元素与辅助栈栈顶元素进行比较
// 当栈顶元素小于待添加元素 -> 辅助栈添加栈顶元素
// 当栈顶元素大于待添加元素 -> 辅助栈添加待添加元素
// !! 题目默认各种操作合法:即不回对空栈进行top、min和 pop 操作,所以代码中没有进行相关判定
class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
m_stk.push(x);
if(min_stk.empty()) min_stk.push(x);
else min_stk.push(std::min(min_stk.top(), x));
}
void pop() {
m_stk.pop();
min_stk.pop();
}
int top() {
return m_stk.top();
}
int min() {
return min_stk.top();
}
private:
stack<int> min_stk;
stack<int> m_stk;
};[232] https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/ 🌟🌟
// 解题思路:
// (1) 申请两个栈 data_stack 和 m_stack
// (2) 当入队(添加数据)时, 执行如下三个步骤
// - 将 data_stack 中的数据逐个 放到 m_stack 中
// - 将 value 添加到 m_stack 中
// - 将 m_stack 中的数据 逐个放入到 data_stack 中
// (3) 当出队(删除数据)时, 直接弹出 data_stack 栈顶数据即可
private:
stack<int> data_stack;
stack<int> m_stack;
public:
CQueue() {
}
void appendTail(int value) {
while(!data_stack.empty()){
m_stack.push(data_stack.top());
data_stack.pop();
}
data_stack.push(value);
while(!m_stack.empty()){
data_stack.push(m_stack.top());
m_stack.pop();
}
}
int deleteHead() {
if(data_stack.empty()) return -1; // 边界条件! 栈空!
int x = data_stack.top();
data_stack.pop();
return x;
}[225] 用队列实现栈 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/ 🌟🌟
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
if(data_queue.empty()) data_queue.push(x);
else{
while(!data_queue.empty()){
temp_queue.push(data_queue.front());
data_queue.pop();
}
data_queue.push(x);
while(!temp_queue.empty()){
data_queue.push(temp_queue.front());
temp_queue.pop();
}
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int x = data_queue.front();
data_queue.pop();
return x;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
return data_queue.front();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return data_queue.empty();
}
private:
queue<int> data_queue;
queue<int> temp_queue;[946] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-stack-sequences/
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
stack<int> m_stk;
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < pushed.size(); i++){
m_stk.push(pushed[i]);
while(!m_stk.empty() && m_stk.top() == popped[j]){
j++;
m_stk.pop();
}
}
return m_stk.empty();
}类型二: 利用容器实现某种功能
[215] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/
// 查找最大 k 个值: 用最小堆, 声明的第三个类型是 greater<int>
// 查找最小 k 个值: 用最大堆, 声明的第三个类型是 less <int>
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > min_heap;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
if(i < k) min_heap.push(nums[i]);
else{
if(nums[i] > min_heap.top()){
min_heap.pop();
min_heap.push(nums[i]);
}
}
}
return min_heap.top();
}[lcci 17.14] 最小K个数 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/smallest-k-lcci/ 🌟🌟
类题 : 347 Top K Frequent Elements —> 可以使用哈希表解决
// 和 leetcode 215 几乎一样, 最小值, 用最大堆!!
vector<int> smallestK(vector<int>& arr, int k) {
vector<int> res;
if(arr.size() == 0 || k == 0) return res;
priority_queue<int> max_heap; // 最大堆
for(int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++){
if(i < k) max_heap.push(arr[i]);
else{
if(arr[i] < max_heap.top()){
max_heap.pop();
max_heap.push(arr[i]);
}
}
}
while(!max_heap.empty()){
res.push_back(max_heap.top());
max_heap.pop();
}
return res;
}[259] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-median-from-data-stream/ 🌟🌟
// ! 非常经典的一道题目, 借助数据结构,降低算法复杂度
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MedianFinder() {
}
void addNum(int num) {
// 确保加入之后,最大堆的元素值都是小于最小堆的
max_heap.push(num);
min_heap.push(max_heap.top());
max_heap.pop();
// 平衡两个堆得元素个数
while(min_heap.size() > max_heap.size()){
max_heap.push(min_heap.top());
min_heap.pop();
}
}
double findMedian() {
return max_heap.size() > min_heap.size() ? double(max_heap.top())
: (max_heap.top() + min_heap.top()) * 0.5;
}
private:
// 保持大顶堆的元素数目大于小顶堆得元素数目
priority_queue <int> max_heap; // 大顶堆
priority_queue <int, vector<int>, greater<int> > min_heap; // 小顶堆类型三: 单调栈/队列
[lcof 59] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/dui-lie-de-zui-da-zhi-lcof/
// ! 使用单调的双向队列
public:
MaxQueue() {
}
int max_value() {
if(max_deq.size() == 0) return -1;
return max_deq.front();
}
void push_back(int value) {
data.push(value);
while(max_deq.size() && max_deq.back() < value)
max_deq.pop_back();
max_deq.push_back(value);
}
int pop_front() {
if(data.size() == 0) return -1;
int n = data.front();
data.pop();
if(max_deq.size() && max_deq.front() == n)
max_deq.pop_front();
return n;
}
private:
queue<int> data;
deque<int> max_deq;[739] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/daily-temperatures/
vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& T) {
stack<int> m_stk;
vector<int> m_vec(T.size(), 0);
for(int i = 0; i < T.size(); i++){
if(m_stk.empty()) m_stk.push(i);
else{
while(!m_stk.empty() && T[i] > T[m_stk.top()]){
m_vec[m_stk.top()] = i - m_stk.top();
m_stk.pop();
}
m_stk.push(i);
}
}
while(!m_stk.empty()){ // 其实这几行不需要, 初始化就是 0
m_vec[m_stk.top()] = 0;
m_stk.pop();
}
return m_vec;
}[239] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sliding-window-maximum/ 🌟🌟🌟
// ! 使用了单调双向队列: 这是经常考查的重点
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
vector<int> res;
deque<int> m_deque;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
while(!m_deque.empty() && nums[i] > nums[m_deque.back()]){
m_deque.pop_back();
}
m_deque.push_back(i); // 这里进入队列的是 index, 而不是 value
if(i - m_deque.front() >= k) m_deque.pop_front();
// 开始添加!
if(i >= k-1) res.push_back(nums[m_deque.front()]);
}
return res;
}[42] 接雨水 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/ 🌟🌟🌟
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
if(height.size() <= 2) return 0;
int res = 0;
// 首先找到最高的值的下标
int max_ind = max_element(height.begin(), height.end()) - height.begin();
// 从左向右开始遍历:如果当前值比(之前的最大值)的小,那么可以积雨水; 否则更新当前值
int cur = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < max_ind; i++){
if(height[i] < height[cur]) res += (height[cur] - height[i]);
else cur = i;
}
// 从右向左开始遍历
cur = height.size() - 1;
for(int i = cur - 1; i > max_ind; i--){
if(height[i] < height[cur]) res += (height[cur] - height[i]);
else cur = i;
}
return res;
}[84] Largest Rectangle in Histogram https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/description/ 🌟🌟🌟
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
int cur_area = 0;
stack<int> m_stk;
// (1) 让最后的栈内元素都可以弹出 !
heights.push_back(0);
for(int i=0; i < heights.size(); i++){
// (1) 当当前的值比栈顶元素小的时候, 可以计算以栈顶元素为高的最大矩形的长度
while(!m_stk.empty() && heights[i] < heights[m_stk.top()]){
int height = heights[m_stk.top()]; // 高
m_stk.pop();
// 当前的元素 和 弹出元素后的栈顶 差值为 宽
// 注意! 弹出后可能栈为空
int width = m_stk.empty() ? i : i - m_stk.top() - 1;
cur_area = max(height * width, cur_area);
}
m_stk.push(i);
}
return cur_area;
}
// 最大矩形
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {
if(matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0) return 0;
int n = matrix[0].size();
int max_area = 0;
vector<int> heights(n, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < matrix[0].size(); j++){
if(matrix[i][j] == '1') heights[j]++;
else heights[j] = 0;
}
max_area = max(largestRectangleArea(heights), max_area);
}
return max_area;
}3. 链表
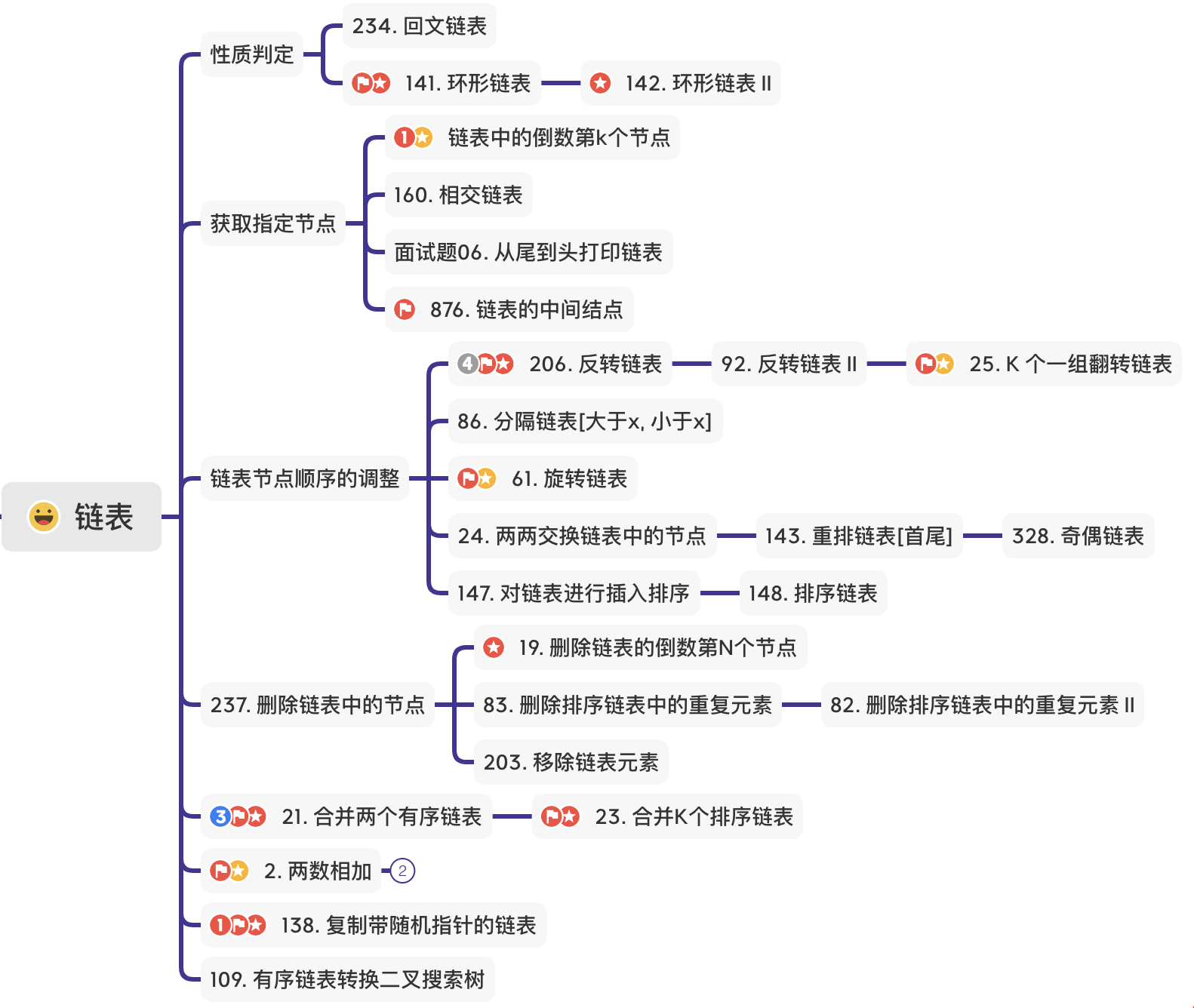
(1) 常用技巧总结
添加哑节点
// 建立 ListNode * dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy -> next = head; // 释放: ListNode * res = dummy -> next; delete dummy; return res;头指针一般不可以随意改变, 可以申请一个指向头指针的指针
ListNode * p = head;不要让链表断开了, 适当的在纸上模拟一下对应的链表指向操作。
注意一下常见的边界条件:头结点 和 尾结点, 链表为空, 只有一个节点。
使用快慢指针、建立一个 Node2index 的 映射
注意些小细节:删除节点的释放,末尾指针不要乱指
(2) 典型例题
① 性质判定
[141] https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/ 🌟🌟
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL) return false;
ListNode * slow = head; // (1) 两个节点初始时候均指向 head
ListNode * fast = head;
while(fast && fast -> next){
// (2) 先移动, 再判断
slow = slow -> next;
fast = fast -> next -> next;
if(slow == fast) return true;
}
return false;
}[142] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/ 🌟🌟
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode * slow = head;
ListNode * fast = head;
while(fast && fast -> next){
slow = slow -> next;
fast = fast -> next -> next;
if(fast == slow) break;
}
if(fast == NULL || fast -> next == NULL)
return NULL;
// (3) 一个指针从相遇节点开始, 另一个指针从头开始,两者如果相遇
// 则该节点即为入环节点
slow = head;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow -> next;
fast = fast -> next;
}
return fast;
}[234] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/
ListNode * reverseLinkList(ListNode * head){
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode * prev = NULL;
ListNode * cur = head;
while(cur){
ListNode * next = cur -> next;
cur -> next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
// (1) 找到中间节点
ListNode * p = head;
int cnt = 0;
while(p){
cnt += 1;
p = p -> next;
}
cnt /= 2;
p = head;
while(cnt--) p = p -> next;
// (2) 翻转后半部分
ListNode * q = reverseLinkList(p);
// (3) 判断是否相等
while(q && head){
if(head -> val != q -> val) return false;
q = q -> next;
head = head -> next;
}
return true;
}②获取指定节点
[19] https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/ 🌟🌟
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy -> next = head;
ListNode * fast = dummy;
ListNode * slow = dummy;
// (1) fast 多走一步, slow 少走一步
for(int i = 0; i < n+1; i++){
fast = fast -> next;
}
while(fast){
fast = fast -> next;
slow = slow -> next;
}
// (2) 释放删除节点
ListNode * del = slow -> next;
slow -> next = slow -> next -> next;
delete del;
// (3) 释放申请的 ListNode
ListNode * res = dummy -> next;
delete dummy;
return res;
}[160] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/ 🌟🌟
int getLengh(ListNode * head){
ListNode * cur = head;
int cnt = 0;
while(cur){
cnt += 1;
cur = cur -> next;
}
return cnt;
}
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
int lenA = getLengh(headA);
int lenB = getLengh(headB);
int diff = abs(lenB - lenA);
ListNode * pA = headA;
ListNode * pB = headB;
if(lenA > lenB){
for(int i = 0; i < diff; i++) pA = pA -> next;
}else{
for(int i = 0; i < diff; i++) pB = pB -> next;
}
while(pA && pB && pA != pB){
pA = pA -> next;
pB = pB -> next;
}
if(pA == NULL || pB == NULL) return NULL;
return pA;
}③ 链表节点顺序的调整
[206] https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list 🌟🌟🌟
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode * prev = NULL;
ListNode * cur = head;
while(cur){
ListNode * next = cur -> next;
cur -> next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}[328] https://leetcode.com/problems/odd-even-linked-list/
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode * oddhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode * evenhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode * p_odd = oddhead;
ListNode * p_even = evenhead;
ListNode * p = head;
int index = 0;
while(p){
if(index % 2 == 0){
p_even -> next = p;
p_even = p_even -> next;
}else{
p_odd -> next = p;
p_odd = p_odd -> next;
}
p = p -> next;
index += 1;
}
p_even -> next = oddhead -> next;
p_odd -> next = NULL; // !! 不要忘记将这个链表 next 置零 <--- 否则会产生死循环! 计算超时
// ! 删除申请的结点
delete evenhead;
ListNode * res = oddhead -> next;
delete oddhead;
return evenhead -> next;
}[86] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-list/ 🌟🌟
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode * before = new ListNode(0);
ListNode * p1 = before;
ListNode * after = new ListNode(0);
ListNode * p2 = after;
ListNode * p = head;
while(p){
if(p -> val < x){
p1 -> next = p;
p1 = p1 -> next;
}else{
p2 -> next = p;
p2 = p2 -> next;
}
p = p -> next;
}
p1 -> next = after -> next;
p2 -> next = NULL;
return before -> next;
}[143] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reorder-list/
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return;
// 获取链表长度
ListNode * p = head;
int len = 0;
while(p){
len++;
p = p -> next;
}
// 翻转后半部分
int mid = len / 2;
p = head;
while(mid--) p = p -> next;
ListNode * rhead = reverseList(p->next);
p -> next = NULL; // !!!
// 合并两个链表
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode * ptr = dummy;
while(rhead && head){
ptr -> next = head;
head = head -> next;
ptr = ptr -> next;
ptr -> next = rhead;
rhead = rhead -> next;
ptr = ptr -> next;
}
if(rhead != NULL) ptr -> next = rhead;
if(head != NULL) ptr -> next = head;
head = dummy -> next;
}[61] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-list/
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
int cnt = 1;
ListNode * ptr = head;
while(ptr -> next){
ptr = ptr -> next;
++cnt;
}
// 做环
ptr -> next = head;
// 移动
k = cnt - k % cnt;
while(k-1){
k--;
head = head -> next;
}
// 修改指针
ptr = head;
head = head -> next;
ptr -> next = NULL;
return head;
}[24]. 两两交换链表中的节点 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/ 🌟🌟
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy -> next = head;
ListNode * prev = dummy;
ListNode * cur = prev -> next;
while(cur && cur -> next){
ListNode * next = cur -> next -> next;
// 翻转
prev -> next = cur -> next;
cur -> next -> next = cur;
cur -> next = next;
// 移动
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return dummy-> next;
}[92] 反转链表 II https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/ 🌟🌟
ListNode * reverseLists(ListNode * head){
if(head == NULL || head -> next == NULL) return head;
ListNode * prev = NULL;
ListNode * cur = head;
while(cur){
ListNode * next = cur -> next;
cur -> next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy -> next = head;
// 查找翻转之前的节点, 记录为 prev
ListNode * pNode = dummy;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < m-1; i++) pNode = pNode -> next;
ListNode * prev = pNode;
// 记录翻转之后的节点, 记录为 next
for(; i < n; i++) pNode = pNode -> next;
ListNode * next = pNode -> next;
pNode -> next = NULL;
// 翻转
ListNode * newhead = reverseLists(prev -> next);
prev -> next = newhead;
// 连接断掉的链表
while(prev -> next) prev = prev -> next;
prev -> next = next;
return dummy -> next;
}④ 删除链表中的节点
[237] https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
node -> val = node -> next -> val;
node -> next = node -> next -> next;
}[面试题 02.01] 移除重复节点 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicate-node-lcci/
ListNode* removeDuplicateNodes(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head -> next == NULL) return head;
set<int> m_set = { head->val };
ListNode * prev = head;
ListNode * cur = head -> next;
while(cur){
if(m_set.find(cur -> val) == m_set.end()){
m_set.insert(cur->val);
prev = cur;
}else{
prev -> next = cur -> next;
}
cur = cur -> next;
}
return head;
}[203] https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
// 添加哑节点
ListNode * newhead = new ListNode(0);
newhead -> next = head;
ListNode * p = newhead;
while(p -> next){
if(p -> next -> val == val){
ListNode * tmp = p -> next;
p -> next = p -> next -> next;
delete tmp; // 删除无用节点
}
else
p = p -> next;
}
return newhead -> next;
}[83] https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/ 🌟🌟
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy -> next = head;
ListNode * ptr = head;
while(ptr && ptr -> next){
if(ptr->val == ptr->next->val){
ListNode * tmp = ptr -> next;
ptr -> next = ptr -> next -> next;
delete tmp;
}else{
ptr = ptr -> next;
}
}
return dummy -> next;
}[82] 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy -> next = head;
ListNode * prev = dummy;
ListNode * cur = head;
while(cur && cur -> next){
ListNode * next = cur -> next;
if(cur -> val != next -> val){
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}else{
while(next && cur -> val == next -> val) // 找到下一个非重复字符
next = next -> next;
prev -> next = next == NULL ? NULL : next;
cur = next;
}
}
return dummy -> next;
}⑤ 合并有序链表
[21] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/ 🌟🌟🌟🌟
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode * newhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode * p = newhead;
ListNode * p_l1 = l1, * p_l2 = l2;
while(p_l1 && p_l2){
if(p_l1 -> val > p_l2 -> val){
p -> next = p_l2;
p_l2 = p_l2 -> next;
p = p -> next;
}else{
p -> next = p_l1;
p_l1 = p_l1 -> next;
p = p -> next;
}
}
if(p_l1 == NULL) p->next = p_l2;
else p-> next = p_l1;
// 注意: 这里要删除申请的 new head 节点, 否则会产生内存泄漏
ListNode * res = newhead;
delete newhead;
return res;
}[23] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/ 🌟🌟🌟
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
if(lists.size() == 0) return NULL;
if(lists.size() == 1) return lists[0];
if(lists.size() == 2) return mergeTwoLists(lists[0], lists[1]);
int len = lists.size();
int mid = len / 2;
vector<ListNode* > lists1;
vector<ListNode* > lists2;
for(int i = 0; i < mid; i++) lists1.push_back(lists[i]);
for(int i = mid; i < len; i++) lists2.push_back(lists[i]);
ListNode * p1 = mergeKLists(lists1);
ListNode * p2 = mergeKLists(lists2);
return mergeTwoLists(p1, p2);
}⑥ 模拟数学运算(两数相加、链表+1)
[2] https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers/
// 模拟常见的加法操作: 需要注意,当一条链表为空时候,仍然在此框架下相加,最后还需要添加 c_in
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode * p = dummy;
int c_in = 0;
while(l1 != NULL || l2 != NULL){
int val1 = l1 != NULL ? l1 -> val : 0;
int val2 = l2 != NULL ? l2 -> val : 0;
int res = val1 + val2 + c_in;
ListNode * newNode = new ListNode(res % 10);
c_in = res / 10;
p -> next = newNode;
p = p -> next;
if(l1 != NULL) l1 = l1 -> next;
if(l2 != NULL) l2 = l2 -> next;
}
if(c_in){
ListNode * newNode = new ListNode(c_in);
p -> next = newNode;
p = p -> next;
}
return dummy -> next;
}[445] 两数相加 II https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers-ii/
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if(l1 == NULL || l2 == NULL) return l1 == NULL ? l2 : l1;
stack<int> stk_1,stk_2;
while(l1){
stk_1.push(l1 -> val);
l1 = l1 -> next;
}
while(l2){
stk_2.push(l2 -> val);
l2 = l2->next;
}
int c_in = 0;
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode * ptr = dummy;
while(!stk_1.empty() || !stk_2.empty()){
int n1 = stk_1.empty() ? 0 : stk_1.top();
int n2 = stk_2.empty() ? 0 : stk_2.top();
int s = n1 + n2 + c_in;
ListNode * pNode = new ListNode(s % 10);
c_in = s / 10;
// 头插法: 可以反向插入节点
pNode -> next = ptr -> next;
ptr -> next = pNode;
if(!stk_1.empty()) stk_1.pop();
if(!stk_2.empty()) stk_2.pop();
}
if(c_in){
ListNode * pNode = new ListNode(c_in);
pNode -> next = ptr -> next;
ptr -> next = pNode;
}
ListNode* res = dummy->next;
delete dummy;
return res;
}[369] https://leetcode.com/problems/plus-one-linked-list/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode * reverseList(ListNode * head){
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode * prev = NULL;
while(head){
ListNode * next = head -> next;
head -> next = prev;
prev = head;
head = next;
}
return prev;
}
ListNode* plusOne(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
head = reverseList(head);
int c_in = 1;
ListNode * ptr = head;
ListNode * prev = head;
while(ptr){
int res = ptr -> val + c_in;
c_in = res / 10;
ptr -> val = res % 10;
prev = ptr;
ptr = ptr -> next;
}
if(c_in) prev -> next = new ListNode(1);
return reverseList(head);
}
};[148] 排序链表 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list/ 🌟🌟🌟
// 复杂度 nlogn 的链表排序
ListNode* merge(ListNode * p1, ListNode * p2){
if(p1 == NULL) return p2;
if(p2 == NULL) return p1;
if(p1 -> val > p2 -> val){
p2 -> next = merge(p2->next, p1);
return p2;
}else{
p1 -> next = merge(p1->next, p2);
return p1;
}
return NULL;
}
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head -> next == NULL) return head;
ListNode * fast = head;
ListNode * slow = head;
ListNode * pre = head;
while(fast && fast -> next){
pre = slow;
fast = fast -> next -> next;
slow = slow -> next;
}
pre -> next = NULL;
return merge(sortList(head), sortList(slow));
}⑦ 复杂链表的复制 🌟🌟🌟🌟
// (1) 存储原链表的 node -> index map
// (2) 数组存储新建的 结点
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
map<Node*, int> node_map;
vector<Node *> node_vec;
Node * ptr = head;
int i = 0;
while(ptr){
node_vec.push_back(new Node(ptr->val));
node_map[ptr] = i;
ptr = ptr -> next;
i += 1;
}
node_vec.push_back(0);
ptr = head;
i = 0;
while(ptr){
node_vec[i] -> next = node_vec[i+1]; // next
if(ptr->random){ // random
node_vec[i] -> random = node_vec[node_map[ptr->random]];
}
ptr = ptr -> next;
i += 1;
}
return node_vec[0];
}4. 树和二叉树
(1) 基础题型总结
- [遍历] 前序、中序、后序、层序遍历(常规、按层、之字型)
- [性质判定] 最大深度、最小深度、对称二叉树、翻转二叉树、相同的树、平衡树、左叶子之和
- [公共祖先] 最近公共祖先(二叉树、二叉搜索树)
- [路径和] 二叉树的路径和、所有路径、最大路径
- [vector 和 tree 交互] 序列化和反序列化二叉树、有序链表重建二叉搜索树、重建二叉树
一些常规思路:
leetcode的测试集经常会有 [] , [0],所以很多题目先要考虑判断是否为空,return None 或者 return [ ]。
时刻要考虑这个节点是否为空, 空节点是不能访问左子树和右子树的。
当返回值非 void 时,考虑到递归的返回值问题,大部分需要设置一个 helper 函数。但是不是绝对,可以利用这个返回值。
递归的基本思想
def func(root): if 满足条件: 退出或进行相关操作 // 相关操作1; func(root->left); // 递归左子树 // 相关操作2; func(root->right); //递归右子树 // 相关操作3;递归相较于迭代:浪费资源反复调用函数
- 递归是一个树结构,每个分支都探究到最远,发现无法继续的时候往回走,每个节点只会访问一次
- 迭代是一个环结构,每次迭代都是一个圈,不会拉掉其中的某一步,然后不断循环,每个节点都会被循环访问
思考的顺序:
- 关于递归:退出条件、递归任务、返回值
- 关于子树:根节点、左子树、右子树
- 关于特殊条件处理:节点 root 为空, 叶子节点
root->left && root->right为空、 单子树为空root->left || root->right、正常节点
(2) 典型例题
类型一. 遍历
[144] 二叉树的前序遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/ 🌟🌟
// 前序
// 递归写法
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
helper(root, res);
return res;
}
void helper(TreeNode * root, vector<int>& res){
if(root == NULL) return;
res.push_back(root->val);
helper(root->left, res);
helper(root->right, res);
}
// 迭代写法
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode * p = root;
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode *> m_stack;
while(p || !m_stack.empty()){
if(p){ // 如果当前节点不空,将其入栈, 并移动指针到左节点
m_stack.push(p);
res.push_back(p->val); // 在此写入结果
p = p -> left;
}else{ // 否则将栈顶弹出,其值写入结果,并将指针指向其右节点
p = m_stack.top();
m_stack.pop();
p = p -> right;
}
}
return res;
}[94] 二叉树的中序遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
// 中序
//递归解法
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
helper(root, res);
return res;
}
void helper(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& res){
if(root == NULL) return;
helper(root->left, res);
res.push_back(root->val);
helper(root->right, res);
}
// 迭代写法:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode * p = root;
stack<TreeNode *> m_stack;
vector<int> res;
while(p || !m_stack.empty()){
if(p){ // 如果当前节点不空,将其入栈, 并移动指针到左节点
m_stack.push(p);
p = p->left;
}else{ // 否则将栈顶弹出,其值写入结果,并将指针指向其右节点
p = m_stack.top();
res.push_back(p->val); // 在此写入结果
m_stack.pop();
p = p -> right;
}
}
return res;
}[145] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
// 怎么和层序遍历的代码差不多呀, 把 queue 改为 stack
vector<int> res;
if(root == NULL) return res;
stack<TreeNode *> m_stk;
TreeNode * p = root;
m_stk.push(p);
while(!m_stk.empty()){
TreeNode * cur = m_stk.top();
m_stk.pop();
res.push_back(cur->val);
if(cur -> left) m_stk.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) m_stk.push(cur->right);
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}[102] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/ 🌟🌟
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int> > res;
if(root == NULL) return res;
queue<TreeNode *> m_queue;
m_queue.push(root);
while(!m_queue.empty()){
int n = m_queue.size();
vector<int> raw;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
raw.push_back(m_queue.front() -> val);
if(m_queue.front() ->left) m_queue.push(m_queue.front() -> left);
if(m_queue.front() -> right) m_queue.push(m_queue.front() -> right);
m_queue.pop();
}
res.push_back(raw);
}
return res;
}[lcof 32] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cong-shang-dao-xia-da-yin-er-cha-shu-lcof/
vector<int> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root == NULL) return res;
queue<TreeNode *> m_queue;
m_queue.push(root);
while(!m_queue.empty()){
res.push_back(m_queue.front() -> val);
if(m_queue.front() -> left) m_queue.push(m_queue.front() -> left);
if(m_queue.front() -> right) m_queue.push(m_queue.front() -> right);
m_queue.pop();
}
return res;
}[103] 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int> > res;
if(root == NULL) return res;
deque<TreeNode * > m_deque;
m_deque.push_front(root);
bool flag = true;
while(!m_deque.empty()){
int n = m_deque.size();
vector<int> raw;
if(flag){ // 一个从头出来, 一个从尾部出来
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
raw.push_back(m_deque.front()->val);
if(m_deque.front()->left) m_deque.push_back(m_deque.front()->left);
if(m_deque.front()->right) m_deque.push_back(m_deque.front()->right);
m_deque.pop_front();
}
}else{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
raw.push_back(m_deque.back()->val);
if(m_deque.back()->right) m_deque.push_front(m_deque.back()->right);
if(m_deque.back()->left) m_deque.push_front(m_deque.back()->left);
m_deque.pop_back();
}
}
flag = ! flag;
res.push_back(raw);
}
return res;
}[199] 二叉树的右视图 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root == NULL) return res;
queue<TreeNode *> m_queue;
m_queue.push(root);
while(!m_queue.empty()){
int n = m_queue.size();
vector<int> row;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
TreeNode * pNode = m_queue.front();
if(pNode->right) m_queue.push(pNode->right);
if(pNode->left) m_queue.push(pNode->left);
m_queue.pop();
row.push_back(pNode->val);
}
res.push_back(row[0]);
}
return res;
}[230] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
// 中序遍历的第k个元素
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode *> m_stk;
TreeNode * cur = root;
int i = 0;
while(cur || !m_stk.empty()){
if(cur){
m_stk.push(cur);
cur = cur -> left;
}else{
cur = m_stk.top();
i++;
if(i == k) return cur -> val;
m_stk.pop();
cur = cur-> right;
}
}
return -1;
}[lcof 52] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-cha-sou-suo-shu-de-di-kda-jie-dian-lcof/
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
// 反中序遍历, 满足条件即输出
stack<TreeNode *> m_stk;
TreeNode * p = root;
int i = 0;
while(p || !m_stk.empty()){
if(p){
m_stk.push(p);
p = p -> right;
}else
{
p = m_stk.top();
if(++i == k) return p->val;
m_stk.pop();
p = p -> left;
}
}
return 0;
}类型二 性质判定
[111] 二叉树的最小深度 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/ 🌟🌟
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
if(root->left == NULL && root -> right == NULL) return 1;
if(root->left == NULL) return minDepth(root->right) + 1;
if(root->right == NULL) return minDepth(root->left) + 1;
return min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}[104] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return 1 + max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right));
}[226] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-cha-shu-de-jing-xiang-lcof/
TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return root;
exchangeTreeNode(root);
return root;
}
void exchangeTreeNode(TreeNode * root){
if(root == NULL) return;
TreeNode * tmp = root -> left;
root -> left = root -> right;
root -> right = tmp;
exchangeTreeNode(root -> left);
exchangeTreeNode(root -> right);
}[110] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/
int getDepth(TreeNode * root){
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return max(getDepth(root->left), getDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
// 递归的解决方案, 先看退出条件比较好!
if(root == NULL) return true;
int left_depth = getDepth(root->left);
int right_depth = getDepth(root->right);
return abs(left_depth - right_depth) <= 1 && isBalanced(root -> left) && isBalanced(root -> right);
}[101] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/symmetric-tree/
bool helper(TreeNode* left, TreeNode * right){
if(left == NULL && right == NULL) return true;
if(left == NULL || right == NULL) return false;
return left -> val == right -> val && helper(left->left, right->right) && helper(left->right, right->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return true;
return helper(root->left, root->right);
}[100] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/same-tree/
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(p == NULL && q == NULL) return true;
if((p == NULL || q == NULL)) return false;
return p->val == q->val &&
isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
}[98] Validate Binary Search Tree https://leetcode.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/description/
long pre = LONG_MIN; // 超级坑的边界条件
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return true; // 先写退出条件
bool left = isValidBST(root->left); // 左子树
// 中间处理过程
if(pre >= root->val) return false;
else pre = root->val;
bool right = isValidBST(root->right); // 右子树
return left && right;
}[404] 左叶子之和 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/ 🌟🌟
// 递归写法
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int res = 0;
helper(root, false, res);
return res;
}
// 不要捉急,先写一个递归遍历函数, 然后考虑怎么在这个的基础上进行修改
void helper(TreeNode * root, bool flag, int& res){
// 递归退出条件
if(root == NULL) return;
// 满足对应的操作, 执行对应的流程
if(flag && root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
res += root->val;
// 递归遍历两颗子树
helper(root->left, true, res);
helper(root->right, false, res);
}
// 非递归
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
int s;
stack<TreeNode * > m_stk;
TreeNode * p = root;
while(p || !m_stk.empty()){
if(p){
m_stk.push(p);
p = p -> left;
if(p && p -> left == NULL && p -> right == NULL) s += p->val;
}else{
p = m_stk.top();
m_stk.pop();
p = p -> right;
}
}
return s;
}类型三 路径与路径和
[113] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-ii/
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
// 总入口函数规定输入和输出
vector<vector<int> > res;
if(root == NULL) return res;
vector<int > path;
recur(root, path, res, sum);
return res;
}
void recur(TreeNode * root, vector<int>& path, vector<vector<int>>& res, int sum){
// 如果为空, 返回!
if(root == NULL) return;
// 执行操作
path.push_back(root->val);
// 满足条件的操作
if(root->val == sum && root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL){
res.push_back(path);
}
// 两次递归!
recur(root->left, path, res, sum - root->val);
recur(root->right, path, res, sum - root->val);
// 仔细考虑此处是不是应该添加!
path.pop_back();
}[112] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum/
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if(root == NULL) return false;
if(sum == root->val && root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) return true;
bool left = hasPathSum(root->left, sum - root->val);
bool right = hasPathSum(root->right, sum - root->val);
return left || right;
}[129] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/ 🌟🌟🌟
int sumNumbers(TreeNode* root) {
int res = 0;
TreeNode * cur = root;
vector<int> path;
recur(cur, res, path);
return res;
}
void recur(TreeNode * root,int& res, vector<int>& path){
if(root == NULL) return;
path.push_back(root->val);
if(root -> left == NULL && root -> right == NULL){ // 叶子节点
int pathsum = 0;
for(auto n: path) pathsum = pathsum * 10 + n;
res += pathsum;
}
recur(root->left, res, path);
recur(root->right, res, path);
path.pop_back();
}[543] 二叉树的直径 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree/
// 直径是边的长度, 而不是节点数。通过观察可以看出, 这里的直径一定是某个节点的左子树的深度 + 右子树的深度。
// 基于这个逻辑。 可以对求深度的代码进行更改即可
public:
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int max_depth = depth(root);
return res;
}
int depth(TreeNode * root){
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int left = depth(root->left);
int right = depth(root->right);
// 考虑一个问题: 为什么使用后序? 因为要先获得两个子节点的深度
res = max(res, left + right); // (1) 如果不考虑这行, 该函数是求该节点的最大的深度
// (2) 这行是去求之前的最大直径, 和经过该节点的最大路径
return 1 + max(left, right);
}
private:
int res = 0;[124] Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-maximum-path-sum/description/ 🌟🌟🌟
// 这道题目和上一道很类似
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
helper(root);
return res;
}
int helper(TreeNode * root){
// 求 以 root 为出发点的 最大路径和
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int left = helper(root->left);
int right = helper(root->right);
// 分三种情况:
// (1) root->val 根节点
// (2) root->val + max(root->left, roor->right) 根节点 + 左子树 or 右子树
// (3) root->val + root->left + root->left 根节点 + 左子树 + 右子树
int max_path_sum = max(root->val ,
max(root->val + max(left, right),
root->val + left + right)))
res = max(res, max_path_sum);
// 分两种情况:
// (1) 孤立的单一节点
// (2) 根节点 + 左右子树的最大值
return max(root->val, max(left, right) + root->val);
}
int res = INT_MIN;类型四: 重建二叉树
[617] https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-binary-trees/
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* t1, TreeNode* t2) {
if(t1 == NULL) return t2;
if(t2 == NULL) return t1;
TreeNode * pNode = new TreeNode(t1->val + t2->val);
pNode -> left = mergeTrees(t1->left, t2->left);
pNode -> right = mergeTrees(t1->right, t2->right);
return pNode;
}[105] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/ 🌟🌟🌟
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
po = preorder; // 前序序列全局化
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.size(); i++) // 中序序列 map 化
m_map[inorder[i]] = i;
return helper(0, 0, inorder.size()-1); // call
}
TreeNode * helper(int pre_root, int left, int right){
/* pre_root: 根节点在前序遍历中的下表
left: 中序遍历的左侧边界
right: 中序遍历的右侧边界 */
if(left > right) return NULL; // 退出条件
TreeNode * root = new TreeNode(po[pre_root]);
int i = m_map[po[pre_root]]; // 找到根节点在中序遍历 index 作为划分标准
root -> left = helper(pre_root+1, left, i-1);
// 找到右子树的根节点: 前序遍历的根节点的坐标 + 左子树的个数 + 1
root -> right = helper(pre_root + (i-left)+1, i+1, right);
return root;
}
private:
map<int, int> m_map;
vector<int> po;
[108] Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
// 将二叉树和二分查找结合的一道题目
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == NULL) return NULL;
return heler(nums, 0, nums.size()-1);
}
TreeNode* heler(vector<int> nums, int begin, int end){
if(begin > end) return NULL;
int mid = begin + (end - begin) / 2;
TreeNode * root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = heler(nums, begin, mid-1);
root->right = heler(nums, mid+1, end);
return root;
}
};[109] 有序链表转换二叉搜索树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-sorted-list-to-binary-search-tree/ 🌟🌟
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
// 第一遍写的时候,这个条件没有处理好
else if(head -> next == NULL) return new TreeNode(head->val);
ListNode * fast = head;
ListNode * slow = head;
ListNode * prev = head;
while(fast && fast -> next){
prev = slow;
fast = fast -> next -> next;
slow = slow -> next;
}
prev -> next = NULL;
TreeNode * root = new TreeNode(slow->val);
root->left = sortedListToBST(head);
root->right = sortedListToBST(slow->next);
return root;
}类型五:最低公共祖先
[235] https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(p->val > root->val && q->val > root->val){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
}else if(p->val < root->val && q->val < root->val){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
}
return root;
}[236] 二叉树的最近公共祖先 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/ 🌟🌟🌟
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
// exit: 根节点为空, 或者找到 p节点 或者 q节点
if(root == NULL || p == root || q == root) return root;
// 递归式:从根节点的左右子树寻找p、q的节点
TreeNode * left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode * right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
// 判断其祖先位置
if(left && right) return root; // 分别出现在左右子树, 则该节点为最低公共祖先
return left ? left : right;
}5. 图
6. 字典 map 的使用
STL 提供了 Map/MultiMap 和 Unordered Map/Multi-Map 来进行字典操作, 其中前者的底层是红黑树,后者的底层才是 哈希表
进行索引时, 如果没有 key, 则会自动插入 key, 且如果 value 为 int, 则初始化为 0
for k in keys: m_map[k]++;经常会使用数组来代替hashmap, 形成 index -> value 这样一种映射, 这种操作在字符串中尤为常见。
常见的 set/map API
begin() end() empty() size() erase(iterator) erase(key_value) find() s.insert(key_value); // set m[key] = val; // map
[347] 前 K 个高频元素 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
vector<int> res;
map<int, int> m_map;
for(auto n:nums) m_map[n]++; // 如果 key 不存在,则自动添加, 且 value 初始化为 0
// 将 map 转化为 vector 进行排序
vector<pair<int, int> > pair_vec(m_map.begin(), m_map.end());
sort(pair_vec.begin(), pair_vec.end(),
[](pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b){return a.second > b.second;}); // lambda 算子
int i = 0;
for(auto p: pair_vec){
if(i++ < k) res.push_back(p.first);
}
return res;
}[387] 字符串中的第一个唯一字符 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/first-unique-character-in-a-string/
// 不要使用 map, 直接使用 数组 作为 哈希表即可
char firstUniqChar(string s) {
vector<int> dic(26, 0);
for(auto c:s) dic[ c - 'a'] += 1;
for(auto c:s) if(dic[c - 'a'] == 1) return c;
return ' '; // 可以直接 return ' ' 的
}[lcof 57] 和为s的两个数字 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/he-wei-sde-liang-ge-shu-zi-lcof/
// 要求返回下标时 -> 使用哈希表解决
// 返回数值时 -> 使用排序 + 双指针
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
set<int> m_set;
vector<int> res;
for(auto n : nums){
if(m_set.find(target - n) == m_set.end()){
m_set.insert(n);
}else{
res.push_back(n);
res.push_back(target - n);
break;
}
}
return res;
}[242]. 有效的字母异位词 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
vector<char> m_vec(26, 0);
for(auto c:s) m_vec[c-'a']++;
for(auto c:t) m_vec[c-'a']--;
for(int i=0; i < m_vec.size(); i++)
if(m_vec[i] != 0) return false;
return true;
}[49] 字母异位词分组 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/group-anagrams/
vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {
vector<vector<string> > res;
map<string, vector<string> > m_map;
for(auto str: strs){
string ori_str = str;
sort(str.begin(), str.end());
m_map[str].push_back(ori_str);
}
for(auto it:m_map) res.push_back(it.second);
return res;
}[448] 找到所有数组中消失的数字 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-all-numbers-disappeared-in-an-array/
vector<int> findDisappearedNumbers(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> res;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
int index = abs(nums[i]) - 1;
if(nums[index] > 0)
nums[index] = -1 * nums[index];
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
if(nums[i] > 0) res.push_back(i+1);
}
return res;
}7. 特殊结构
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!